Haïti, a rich and impoverished country
Located in the western part of the island of Hispaniola, Haïti is a land imbued with natural, cultural and historical wealth. Unfortunately, behind the beauty of its landscapes, the richness of its culture and the delicacy of its cuisine lies a complex reality marked by the debt of its independence and the persistent interference of third countries, casting a shadow over its stability.
b~The Natural Beauty of Haïti~b
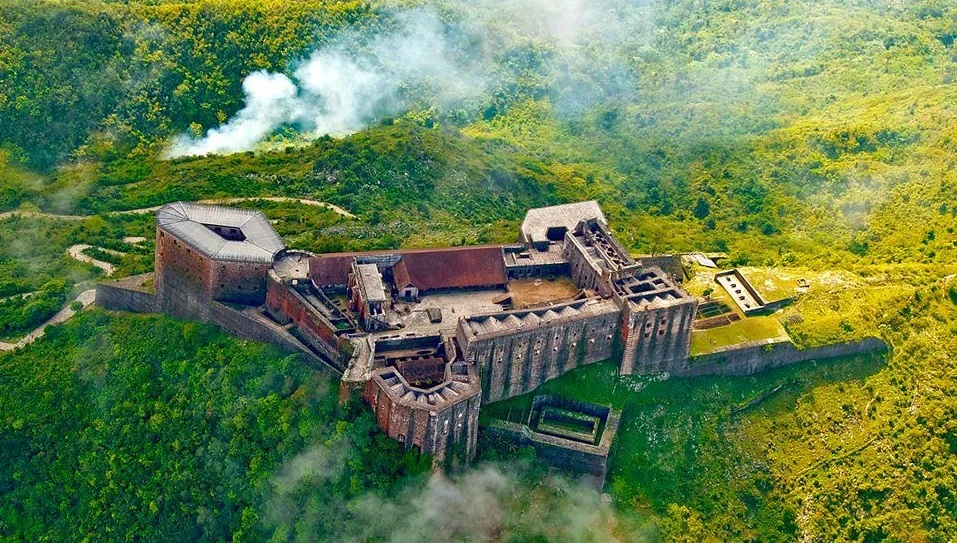
Haïti, nicknamed the "Pearl of the Antilles", dazzles with the diversity of its landscapes. From majestic mountains and lush valleys to meandering rivers and sandy beaches, the country offers natural beauty worth celebrating. The famous Citadelle Laferrière mountains and the refreshing waterfalls of Bassin-Bleu are just a few examples of the splendor that characterizes this nation.
b~A Rich and Diverse Culture~b
Haïti stands out for its vibrant and diverse culture. A heritage of African, French and indigenous influence, Haïtian music, dance and art reflect a unique fusion. Colorful festivals, like Carnival, are celebrations of this cultural richness, attracting visitors from all over the world.
b~Delicious Cuisine~b
Haïtian cuisine, tasty and spicy, is another aspect worth celebrating. Dishes like griot, sticky rice, and the legendary joumou soup, traditionally prepared to commemorate independence, are all culinary delights that demonstrate the country’s gastronomic ingenuity.
b~Heritage Treasures and Paradise Beaches~b
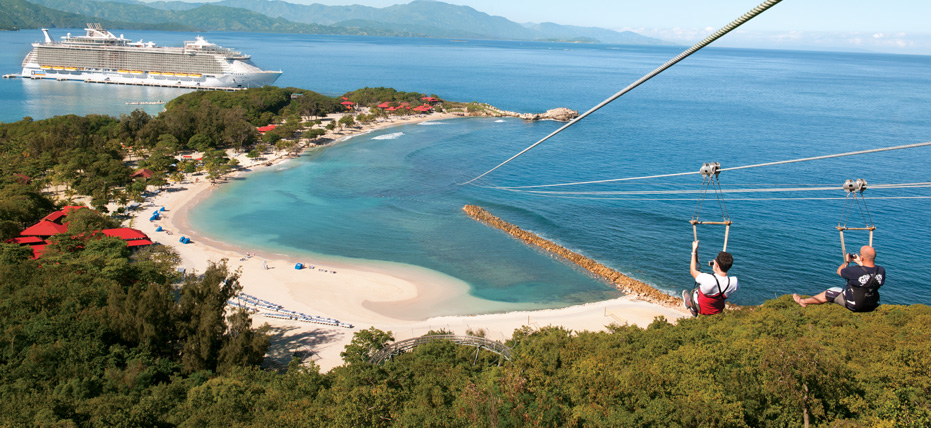
Haïti’s heritage treasures, such as the remains of the Sans-Souci Palace and the Citadelle Laferrière, listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, are testimonies to the architectural grandeur of Haïti’s past. At the same time, beaches like Labadee and Jacmel offer havens of peace with crystal clear waters, attracting travelers in search of a tropical paradise.
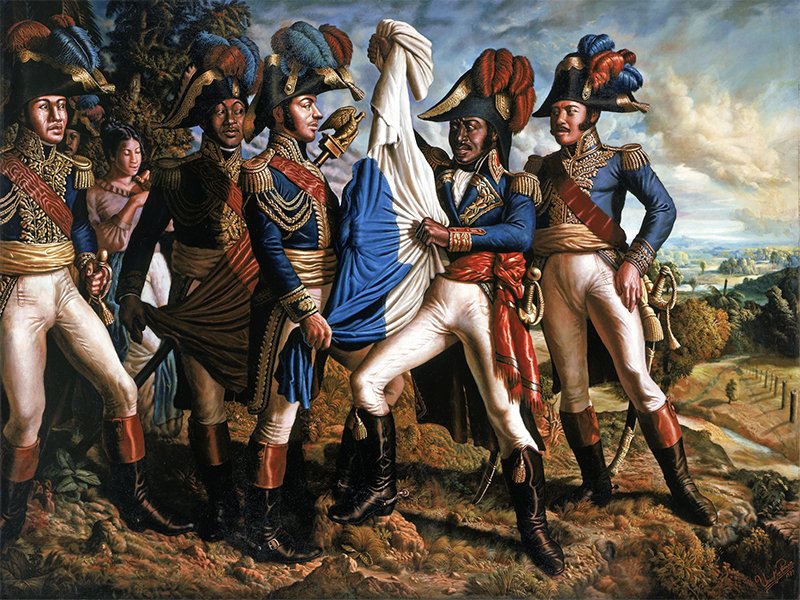
b~A Fascinating Story~b
The history of Haïti is both fascinating and tragic. It was the first country in the Americas to gain its independence, in 1804, after a courageous slave revolt. However, this independence came with a heavy financial price. France demanded exorbitant compensation, thus laying the foundations for Haïti’s foreign debt.
b~The Debt of Independence and Foreign Interference~b
Despite these treasures, Haïti struggles with the reality of its independence debt. After gaining its freedom, the country was forced to pay France a considerable sum in compensation for losses associated with the abolition of slavery. This debt has been a major economic burden for Haïti, hindering its development.
Additionally, foreign interference continues to create significant challenges. External political and economic interventions have often contributed to the country’s instability, hindering its ability to build a sustainable future for its citizens.
b~In conclusion~b
Haïti remains a country of multiple riches, but its challenges persist. Despite its natural beauty, rich culture and fascinating history, the nation needs enlightened international support and lasting solutions to overcome the obstacles that stand in its way. Haïti’s wealth lies not only in its enchanting landscapes, but also in the potential of its people to be resilient and prosper despite persistent challenges.