The literary and philosophical club of Galette-Chambon reveals its second edition: a journey to the heart of books
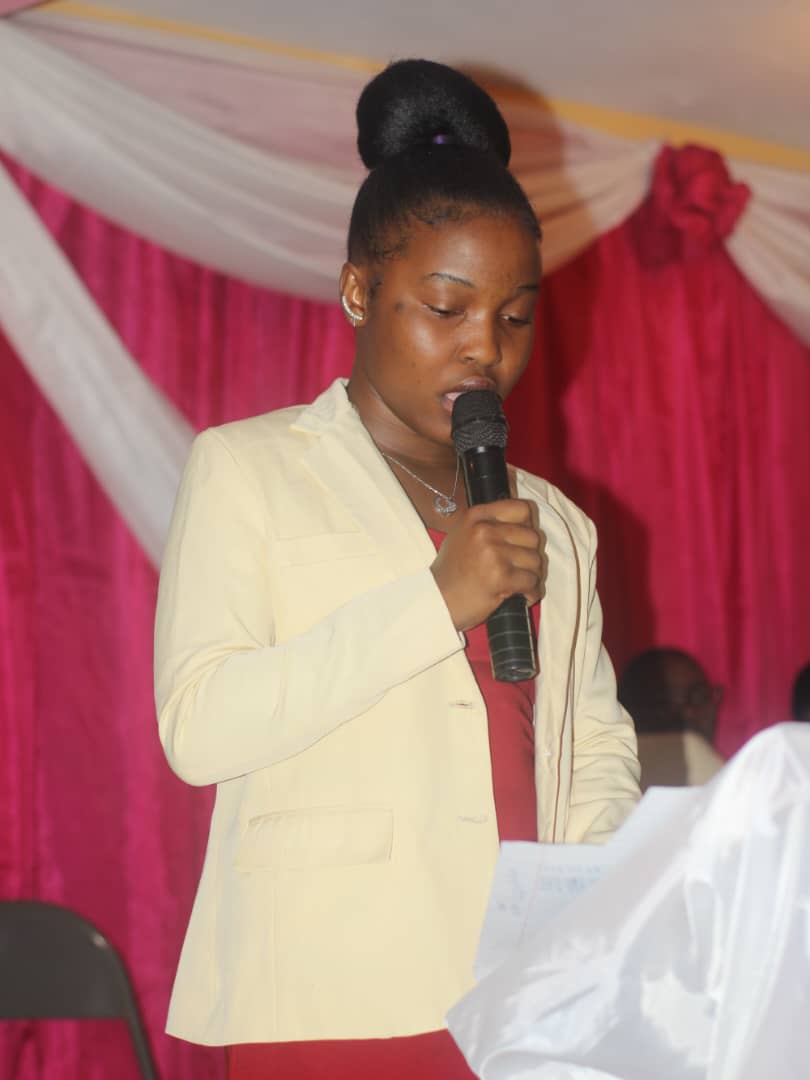
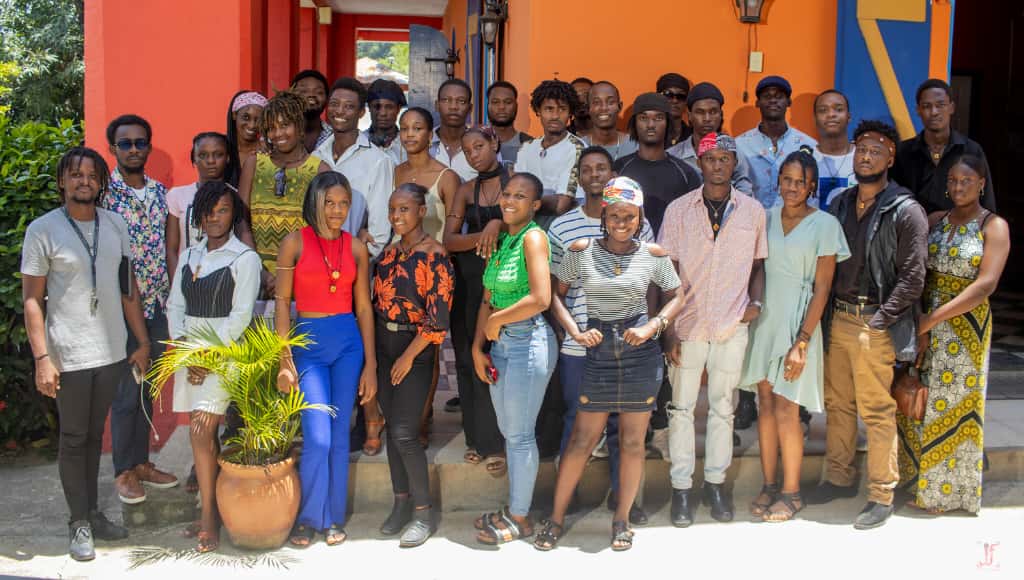
In an atmosphere of madness, at the Auditorium Saint Jean Marie Vianney de Galette-Chambon, where the laughs broke out, the music resounded, and the talents were dismented, started the second edition of the reading competition, around the theme "Ann Li pou n chanje peyi n ». This initiative, organized by the literary and philosophical club of Galette Chambon (CLPGACH) on Friday 06 October 2024, was marked by an overflowing passion within the public. The spectators came for several reasons: to support the applicants and live their presentations.
The works, as "thus spoke of the uncle", "the vocation of the elite" of Jean Price Mars, "the ten black men" of Etzer vilary and "the courage to live in Haïti in the 21st century" of Hérold Toussaint, present innovative arguments linked to the societal context. They intertwine with folklore, Haitian culture, sociology and anthropology. These books are given to the applicants for a period of 15 days. Back, they come with their summaries and, after each presentation, in turn, reveal new perspectives on burning questions and delicate themes from works, while taking into account the concepts learned in public speaking. In this arena where the verve and the verb clash as well as logic, conviction, precision and clarity, it is a question of "saying all in a few words".
The judgments are based on three criteria: the methodology concerning the substance and the form of the work; The eloquence which concerns verbal and non -verbal discourse (micro management, good pronunciation, etc.); And finally, an essential criterion: understanding. This is to assess whether the applicant has controlled the work. Questions can be asked without ignoring the context in which he lives.
In addition, assistants have the opportunity to vote for the applicant who charmed them the most. This vote is precious at a higher level. Note that this vote can be made not only face -to -face but also online on our Facebook page CLPGACH.
In addition, the public has always changed well through this trip to the universe of regional authors. The latter weave the frame and make vital the very repertoire of the competition vital, made up of impactful works such as "the price of irresponsibility" of Montuma Murat, "the return to citizen responsibility" written by Jean Jacquesson Thelucier and "Courage to live in Haïti in the 21st century "Professor Hérold Toussaint, to name a few.
Although they died, some writers still live at the heart of our situation through their inheritance. Among them, it is necessary to quote: "the vocation of the elite" of Doctor Jean Price Mars, "the ten black men" of Etzer Villaire and "the Governor of the dew" by Jacques Roumain, as well as so many others .
For this literary event to be moving and meets expectations for this second edition, many sacrifices are necessary on the part of the staff as well as the public which never leaves us alone. In this sense, we would like to thank them and call all those wishing to support this event.
Indeed, if this competition is a solution found to advance together towards a common goal, its success depends on everyone’s commitment.
About two years ago, the security climate in the area was not conducive to the completion of the competition. Although it is not yet ideal today, it is time to triumph over obscurantism and fight the dictatorship of ambient ignorance.